SEIM Flasher Relay: Role, Functioning, Selection, and Installation
The flasher relay is an essential component of a vehicle's lighting system, as it controls the blinking of turn signal lights. This electronic component regulates the flashing frequency of the indicators, ensuring correct signaling to other road users.
What is a Flasher Relay?
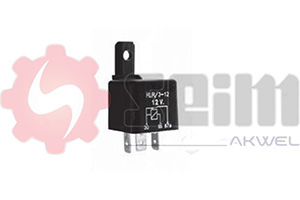
The flasher relay is responsible for the blinking of signaling lights, such as turn signals and sometimes hazard lights. It generates a constant blinking rhythm for the vehicle's front, rear, and side lights, doing so in a synchronized manner. This allows drivers to effectively signal their changes in direction or alert others to a danger using the hazard lights.
Main Functions of the Flasher Relay
- Control of Flashing Frequency: The relay regulates the speed at which the turn signals light up and go out (usually between 60 and 120 times per minute).
- Failure Signaling: In case of a failure of one of the turn signals (burnt bulb), the flasher relay can increase the flashing frequency to indicate a malfunction.
- Control of Hazard Lights: Some relays also control the hazard lights, activating all indicators at a constant rhythm to warn other drivers in emergencies.
Types of Flasher Relays
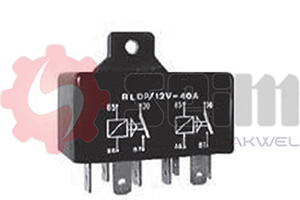
- Electromechanical Relay: The oldest type, using a relay and a thermal element to generate a flashing rhythm. Simple but less precise than modern electronic versions.
- Electronic Relay: Uses circuits to control flashing more precisely and steadily, even with voltage variations in the vehicle's electrical system. Widely used in modern vehicles.
- LED Flasher Relay: Specifically designed for LED lighting systems, suited for the low power consumed by LED bulbs, preventing issues like hyperflash (overly fast flashing).
How to Choose a Flasher Relay?
- Compatibility with the Vehicle: Ensure you select a relay compatible with your vehicle model and specifications to avoid fitting errors.
- Compatibility with the Vehicle's Electrical System: Verify the relay’s compatibility with your vehicle's voltage and power (e.g., 12V or 24V) and bulb type (halogen, LED).
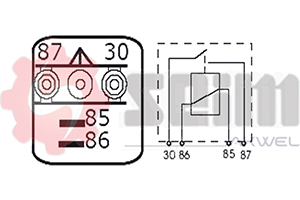
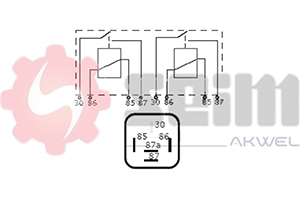
- Type of Relay:
- Electromechanical: Suitable for older vehicles.
- Electronic: Preferred for reliability and compatibility with newer technology.
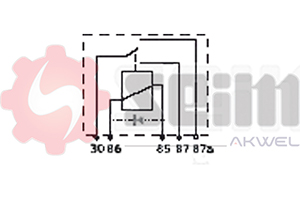
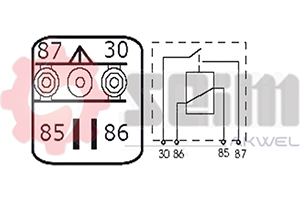
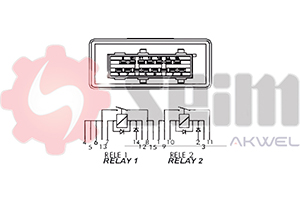
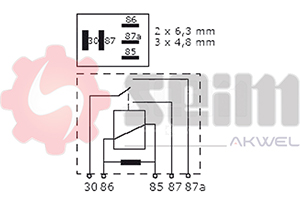
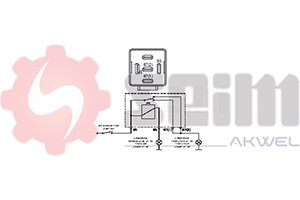
- Number of Pins: Ensure the pin configuration (usually 2, 3, or 4 pins) matches your vehicle's electrical system.
Installation of the Flasher Relay
- Preparation: Disconnect the vehicle battery to avoid any risk of short circuit.
- Location of the Flasher Relay: Often found under the dashboard or near the fuse box; consult your vehicle manual for exact placement.
- Removal of the Old Relay: Carefully disconnect and remove the relay, noting the pin configuration.
- Installation of the New Relay: Connect the new relay, ensuring pins match those of the old one and that the relay is securely fixed to avoid vibrations.
- System Test: Reconnect the battery and test turn signals and hazard lights to ensure proper relay operation.
Maintenance of Flasher Relays
- Cleaning: Keep the relay clean to prevent dirt accumulation that could affect performance.
- Regular Inspection: Periodically check the relay for signs of wear or malfunction.
- Preventive Replacement: Replace the relay at regular intervals as per the manufacturer’s recommendations to avoid unexpected failures.
Discover SEIM Flasher Relays Today!
The flasher relay is an essential component of a vehicle's lighting system, ensuring reliable signaling for direction changes and emergency situations. Contact us today to learn more and discover how our relays help maintain safe and effective signaling.
SEIM - Your Partner for Reliable and High-Performance Solutions