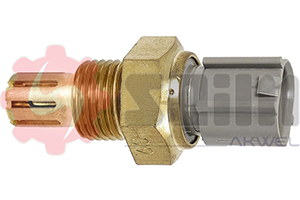
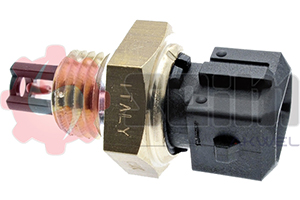
Air Temperature Sensor SEIM: Role, Functioning, Selection, and Installation
The air temperature sensor plays an essential role in electronic engine management. It measures the temperature of the air intake by the engine to adjust the air-fuel mixture. SEIM air temperature sensors are developed to meet the strictest requirements, ensuring stable performance even in the most extreme conditions.
What is an Air Temperature Sensor?
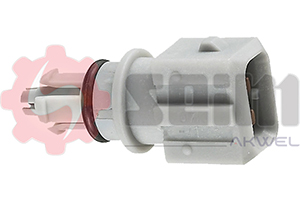
The air temperature sensor, often referred to as the IAT (Intake Air Temperature) sensor, measures the temperature of the air entering the intake system. This information is then sent to the engine control unit (ECU), which adjusts the air-fuel mixture to optimize combustion based on the air density, influenced by temperature.
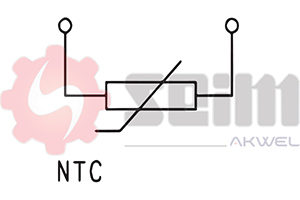
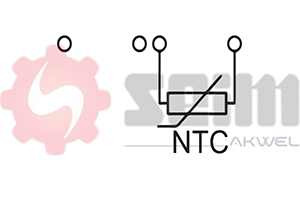
The air temperature sensor uses a thermistor, an electronic component that changes resistance according to temperature. These thermistors can be of two main types, each with a distinct operating mode.
Main Functions of the Air Temperature Sensor
- Optimization of the Air-Fuel Mixture: When the air temperature changes, the ECU adjusts the amount of fuel injected to maintain an optimal mixture and efficient combustion.
- Improvement of Engine Performance: By ensuring that the air-fuel ratio is always correct, the sensor maximizes engine power while minimizing fuel consumption.
- Reduction of Pollutant Emissions: Proper adjustment of the air-fuel mixture helps reduce harmful emissions from the engine.
- Prevention of Engine Anomalies: A faulty sensor can lead to symptoms such as irregular idling, hesitation during acceleration, or excessive fuel consumption.
Types of Thermistors
The sensor operates by using a thermistor, an electronic component whose resistance varies with the air temperature. There are primarily two types of thermistors:
1. NTC Thermistor (Negative Temperature Coefficient)
NTC thermistors are the most commonly used in vehicle air temperature sensors. In an NTC thermistor, resistance decreases as temperature increases. In other words, as the air warms up, the NTC thermistor allows more current to flow, signaling to the ECU a rise in air temperature.
Characteristics of NTC Thermistors:
- High Sensitivity: They provide a quick response to temperature changes, making them ideal for engine management applications.
- Accuracy: They offer precise measurements over a wide temperature range, typically used in engine air intake systems.
- Application: They are present in the majority of air temperature sensors, as they can track rapid fluctuations in air intake temperature, essential for combustion management.
2. PTC Thermistor (Positive Temperature Coefficient)
PTC thermistors, on the other hand, increase their resistance as temperature rises. They are generally not used in engine air temperature sensors but rather in applications where it is necessary to limit or interrupt current in the event of overheating.
Characteristics of PTC Thermistors:
- Overheating Protection: By increasing their resistance, they can cut off electrical power or limit current when a threshold temperature is reached.
- Limited Use in Automotive: Unlike NTC thermistors, PTC thermistors are less suitable for engine air temperature sensors due to their reverse functioning.
How to Choose an Air Temperature Sensor?
- Compatibility with the Vehicle: Like most engine sensors, each vehicle requires a specific sensor. Therefore, it's crucial to choose a sensor that is compatible with your vehicle and the engine model you are using. Check the original references or consult the manufacturer's specifications to avoid compatibility errors.
- Type of Thermistor: Most vehicles use NTC thermistors for their accuracy and sensitivity. Make sure to choose a sensor with an NTC thermistor for optimal engine functioning.
- Temperature Range: Sensors should accurately measure within the air intake temperature range, which can vary from very low temperatures (in cold weather) to high temperatures (when air passes through a turbocharger or intercooler).
Installation of the Air Temperature Sensor
- Preparation: Before proceeding with installation or replacement, disconnect your vehicle's battery to avoid any risk of short circuit or damage to the ECU.
- Locating the Air Temperature Sensor: The sensor is typically located in the intake duct, near the air filter. Consult your vehicle's manual to find the exact location.
- Removing the Old Sensor: Locate the faulty sensor, disconnect the connectors, and remove it following the manufacturer's instructions.
- Installing the New Sensor: Position the new sensor in place, secure it properly, and reconnect the connector.
- Testing Functionality: After installing the sensor, reconnect the battery and start the engine to test its proper functioning. Use an OBD diagnostic tool if necessary to check temperature readings.
Maintenance of Air Temperature Sensors
- Cleaning: Keep the sensors clean to prevent dirt accumulation that could affect their performance.
- Regular Inspection: Check the condition of the sensors regularly to detect any signs of wear or malfunction.
- Preventive Replacement: Replace sensors at regular intervals according to the manufacturer's recommendations to avoid unexpected failures.
Discover SEIM Air Temperature Sensors Now!
The air temperature sensor is essential for optimizing the air-fuel mixture in the engine. Understanding the role of thermistors, particularly NTCs, allows you to choose a sensor suited to your vehicle's needs. Contact us today to learn more and discover how our sensors can ensure optimal engine performance, better fuel consumption, and reduced emissions.
SEIM - Your Partner for Reliable and High-Performance Solutions